Introduction to Wearable Health Tech
Wearable health technology, often referred to as wearable health tech, encompasses a range of electronic devices designed to be worn on the body. These devices primarily include fitness trackers, smartwatches, and biosensors, all of which serve the fundamental purpose of monitoring various health metrics and aiding in the real-time management of wellness. The rapid growth of this industry has been marked by significant advancements in technology, making these devices both more accurate and user-friendly.
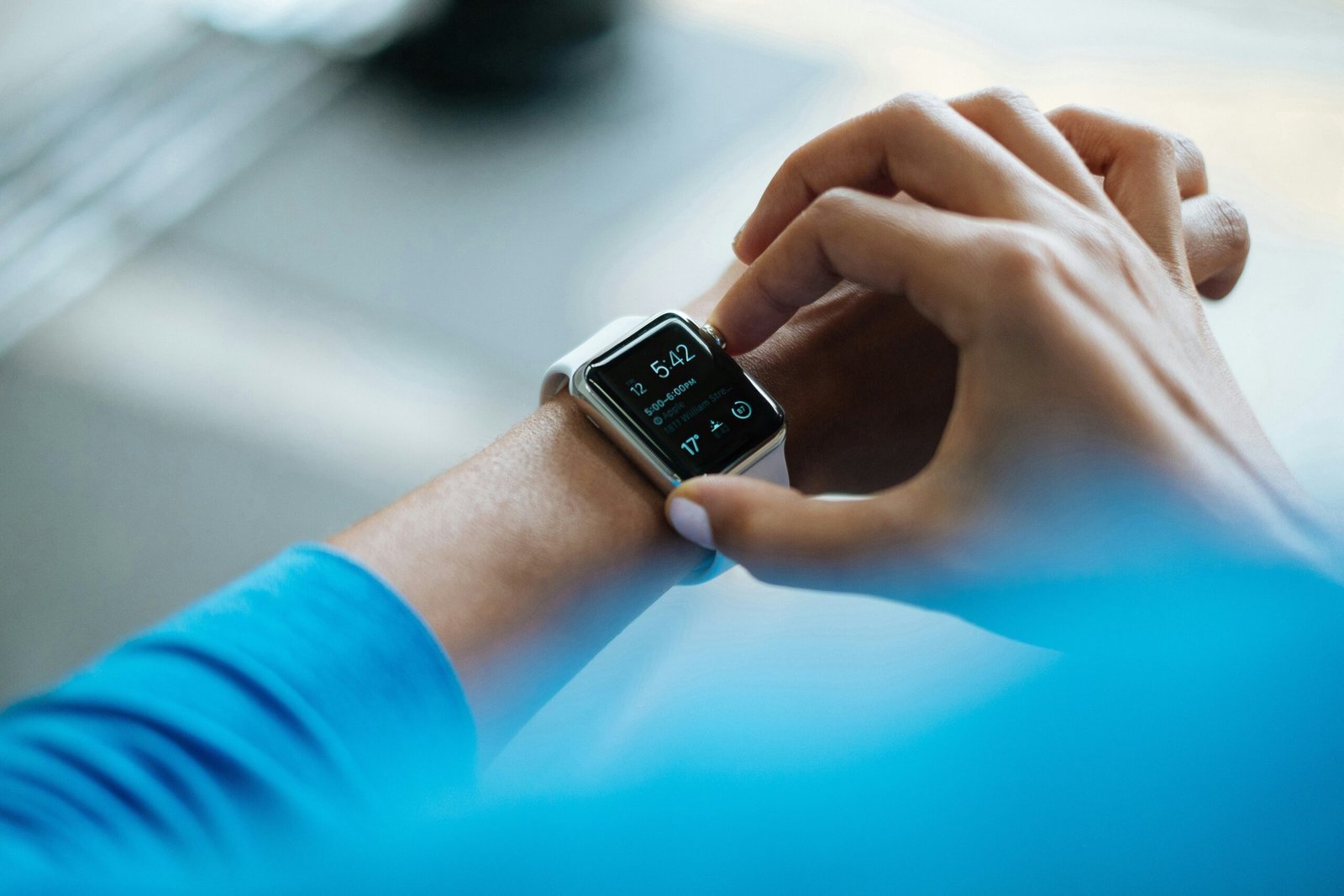
Fitness trackers, for instance, are among the most popular wearable health devices. They typically monitor activities such as steps taken, calories burned, and sleep patterns. Smartwatches not only provide the functionality of fitness trackers but also integrate features such as heart rate monitoring, GPS tracking, and even the ability to receive notifications from a user’s smartphone. Biosensors, on the other hand, are more specialized devices that can measure specific physiological data like glucose levels, blood pressure, and other vital signs.
The increasing adoption rates of wearable health tech among consumers highlight the growing interest in maintaining and improving personal health. This trend is driven by a greater awareness of health and wellness, coupled with the convenience and accessibility provided by these devices. The ability to monitor health metrics continuously and in real-time supports proactive health management, potentially preventing serious health issues before they arise.
Technological advancements have played a crucial role in the evolution of wearable health tech. Innovations in sensor technology, data analytics, and wireless communication have enhanced the accuracy and functionality of these devices, making them indispensable tools for health monitoring. Additionally, improvements in battery life, design, and user interface have made wearable devices more appealing and easier to incorporate into daily life.
In summary, wearable health tech represents a significant leap forward in personal health management. By providing real-time insights and fostering proactive health practices, these devices have the potential to transform the way we approach wellness.
Key Features and Benefits
Wearable health tech devices have transformed the landscape of personal health management by incorporating a range of advanced features. Among the most prominent are heart rate monitoring, sleep tracking, activity tracking, and ECG capabilities. These functionalities provide users with invaluable data to monitor and manage their wellness effectively.
Heart rate monitoring is a fundamental feature in wearable devices. Using photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors, these devices measure the pulse rate by detecting blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue. Continuous heart rate monitoring helps users understand their cardiovascular health, manage stress, and optimize workout intensity. For example, Apple Watch users can receive alerts if their heart rate remains above or below a certain threshold while they appear inactive, prompting them to seek medical attention if necessary.
Sleep tracking leverages accelerometers and other sensors to monitor sleep patterns. By analyzing movements and heart rates, wearables can distinguish between different sleep stages, such as light, deep, and REM sleep. Insights from sleep data help users improve their sleep hygiene, which is crucial for overall health and well-being. Fitbit devices, for instance, provide personalized sleep scores and recommendations for better sleep quality.
Activity tracking is another cornerstone of wearable health tech. These devices use accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS to monitor various physical activities, including steps taken, distance traveled, and calories burned. This data motivates users to achieve their fitness goals by setting daily activity targets. A classic example is the Garmin fitness tracker, which offers diverse activity modes and detailed performance analytics.
ECG capabilities elevate wearable health tech to the next level by allowing users to perform electrocardiograms. With the help of built-in electrodes, devices like the Apple Watch Series 6 can detect irregular heart rhythms and provide early warnings of atrial fibrillation (AFib). This feature is particularly beneficial for users with a history of cardiovascular issues, enabling timely intervention and management.
The benefits of wearable health tech are multifaceted. Improved health awareness, achieved through continuous monitoring and feedback, empowers users to make informed lifestyle choices. The motivation for physical activity is reinforced by real-time tracking and goal-setting features. Additionally, the early detection of potential health issues, facilitated by advanced sensors and alert systems, can lead to prompt medical consultation and treatment. Furthermore, wearable devices enable the seamless sharing of health data with healthcare providers, which is instrumental in managing chronic conditions more effectively.
Real-world examples underscore the transformative impact of wearable health tech. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that patients using wearable devices for remote monitoring exhibited better management of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. This highlights the potential of wearables to enhance patient outcomes through continuous health monitoring and data sharing.
Challenges and Limitations
Wearable health tech has undoubtedly revolutionized the way individuals monitor and manage their wellness. However, it comes with its own set of challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is data accuracy. Wearable devices, though advanced, are not flawless. Variables like sensor placement, user movement, and device calibration can affect the precision of the data collected. Inaccurate data can lead to misinterpretations and potentially impact health decisions adversely.
Privacy concerns are another significant challenge. Wearable health devices collect a vast amount of sensitive health information, which, if not properly secured, can be vulnerable to breaches. Users need assurance that their data is protected from unauthorized access and misuse. This calls for robust cybersecurity measures and transparent data policies from manufacturers and service providers.
Additionally, the constant need for device maintenance, including regular charging, can be an inconvenience. Users must ensure their devices are always operational, which can be particularly challenging for individuals with busy lifestyles. The dependency on these devices also raises concerns, as over-reliance on technology could diminish individuals’ attentiveness to their bodies’ natural signals.
The digital divide further complicates the widespread adoption of wearable health tech. Not everyone has access to these technologies due to high costs or a lack of technological literacy. This gap can lead to health disparities, where only a segment of the population benefits from advanced health monitoring tools. Efforts must be made to make these technologies more affordable and accessible to bridge this divide.
Moreover, there is a delicate balance between technology and human judgment in health management. While wearable health tech provides valuable data, it is crucial for users and healthcare professionals to interpret this data correctly. Misinterpretation can lead to unnecessary anxiety or complacency. Thus, education on how to understand and act on the information provided by these devices is essential.
Future Trends and Innovations
The wearable health tech industry is on the brink of transformative changes, driven by the integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These advancements are set to provide more personalized health insights, tailoring wellness recommendations to individual needs. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of health data to detect patterns and predict potential health issues, thereby enabling proactive management of one’s health.
One of the most exciting developments in this sector is the creation of new types of sensors and materials, designed to make wearable devices more comfortable and versatile. Flexible sensors, for instance, can be embedded in clothing or even directly onto the skin, providing continuous, real-time health monitoring without discomfort. These innovations are not just limited to physical health tracking but extend to mental well-being as well, with devices capable of measuring stress levels and offering relaxation techniques.
Moreover, the integration of wearable health tech with other healthcare technologies promises to create a more cohesive health management system. Devices can now sync seamlessly with telemedicine platforms, allowing healthcare providers to access real-time data and make informed decisions during virtual consultations. Additionally, the synchronization with electronic health records (EHRs) ensures that all health data is centralized, which can significantly enhance the quality of care and reduce medical errors.
Looking ahead, these advancements hold immense potential for further enhancing wellness monitoring and management. The combination of AI-driven insights, flexible and comfortable sensors, and integrated health systems could spearhead a new era of precision medicine. As these technologies evolve, we can anticipate a future where monitoring and managing wellness is not only more efficient but also more personalized, ultimately improving overall health outcomes.