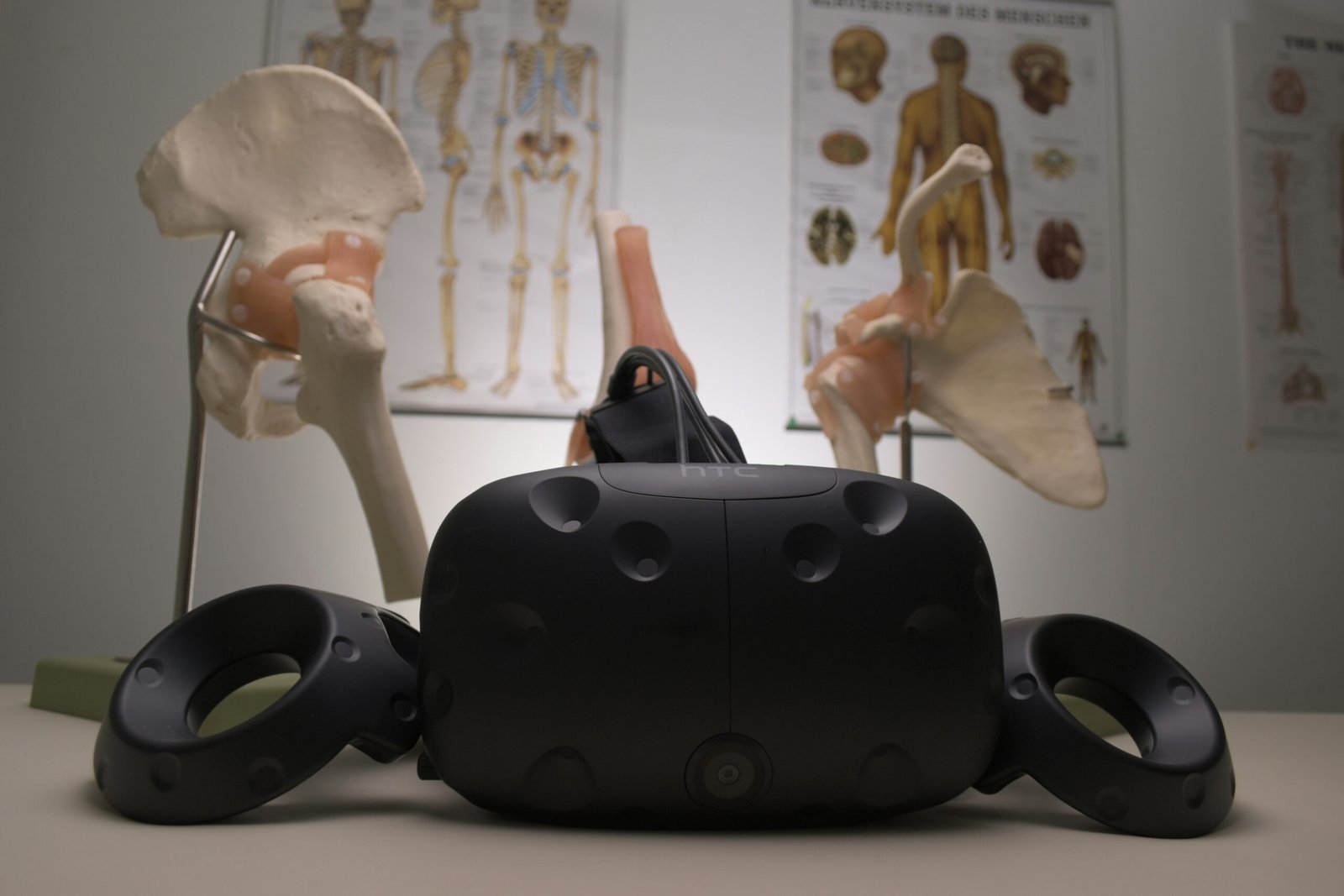
Virtual Reality (VR) technology, initially popularized in the realms of gaming and entertainment, has evolved significantly over the past decade. This advancement has led to its adoption in various professional fields, including healthcare. VR in healthcare leverages immersive, interactive environments to simulate real-world experiences, providing both practitioners and patients with innovative solutions to complex challenges.
One of the primary advantages of VR in the medical field is its capability to improve patient outcomes. By creating controlled, replicable environments, VR allows for precise simulation of medical procedures, enabling surgeons and medical professionals to practice and perfect their skills without the risks associated with real-life surgeries. Furthermore, VR can be used to develop patient-specific simulations, aiding in preoperative planning and increasing the precision of the interventions.
VR also enhances training capabilities within the healthcare sector. Medical students and professionals can utilize VR-based simulations to gain hands-on experience in a variety of scenarios, ranging from routine procedures to rare and complex cases. This immersive training environment supports the development of critical skills and decision-making abilities, thereby improving overall competency and confidence among healthcare providers.
In terms of therapy, VR offers innovative methods for treating various conditions. For instance, VR-based therapies have shown promise in the management of chronic pain, anxiety disorders, and PTSD. These therapies often involve virtual environments that help patients confront and manage their symptoms in a controlled setting, leading to reduced pain and anxiety levels, and improved mental health outcomes.
Current market trends indicate a growing investment in VR technologies by healthcare institutions. As the technology becomes more accessible and its benefits more widely recognized, healthcare providers are increasingly integrating VR into their practices. This trend is supported by ongoing advancements in VR hardware and software, which continue to enhance the effectiveness and usability of VR applications in healthcare.
VR for Medical Training and Education
Virtual reality (VR) is significantly transforming the landscape of medical training and education. Medical schools and hospitals are increasingly integrating VR applications into their curricula to enhance the learning experiences of healthcare professionals. One prominent example is the use of surgical simulations, where aspiring surgeons can practice complex procedures in a risk-free, immersive environment. These simulations provide a detailed, three-dimensional view of the human body, allowing trainees to develop their skills and precision without the immediate pressures of real-life surgery.
Additionally, VR is being employed for anatomy lessons, offering students an unparalleled, interactive learning experience. Traditionally, anatomy has been taught using cadavers, which, while effective, come with limitations such as availability and ethical considerations. In contrast, VR can simulate the human body in intricate detail, allowing students to explore and manipulate anatomical structures in ways that were previously impossible.
Emergency response drills are another area where VR has shown immense potential. VR scenarios can replicate a wide range of emergency situations, from natural disasters to mass casualty events, enabling healthcare professionals to hone their decision-making and procedural skills in a controlled environment. This immersive training can lead to better preparedness and more effective real-world responses.
Several VR training programs have shown promising results in improving the skills and knowledge of medical professionals. For example, studies have demonstrated that VR-based training can enhance surgical proficiency, reduce error rates, and improve overall patient outcomes. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that residents trained with VR performed significantly better in surgical tasks than those trained by traditional methods. Moreover, a survey conducted by the American College of Surgeons revealed that 87% of respondents believed VR training was beneficial and should be incorporated into surgical education.
In essence, VR is revolutionizing medical training by providing realistic, immersive, and repeatable experiences. Its applications in surgical simulations, anatomy lessons, and emergency response drills are proving to be effective in enhancing the skills and knowledge of medical professionals, ultimately leading to better patient care.
Therapeutic Applications of VR in Healthcare
Virtual Reality (VR) has found a significant foothold in therapeutic settings within the healthcare industry. One of the primary therapeutic applications is in pain management. VR has been effectively used to distract patients from chronic pain, reducing their reliance on pain medications. By immersing patients in a calming virtual environment, VR helps to modulate pain perception and improve the overall quality of life. For instance, burn patients undergoing painful wound care have reported substantial relief when engaged with VR distractions.
Another essential therapeutic application of VR is in physical rehabilitation. VR-based rehabilitation programs use interactive 3D environments to create engaging and motivating exercises for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. These programs can be tailored to the individual’s therapy needs, enabling patients to perform repetitive movements crucial for regaining strength and mobility. Studies have demonstrated that VR rehabilitation can improve patient outcomes, adherence to therapy, and overall satisfaction with the recovery process.
In the realm of mental health treatment, VR has shown promise in addressing conditions such as Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and phobias. VR therapy allows patients to confront and manage their fears in a controlled, safe, and gradual manner. For example, VR exposure therapy has been successfully utilized to treat veterans with PTSD by recreating traumatic scenarios in a virtual setting. Patients can slowly desensitize to their triggers under the guidance of a therapist, leading to significant reductions in symptoms.
Feedback from both patients and healthcare providers regarding VR therapy has been overwhelmingly positive. Patients appreciate the immersive and interactive nature of VR, which makes therapy sessions more engaging and less intimidating. Healthcare providers have noted the potential of VR to enhance traditional therapeutic techniques, offering a valuable adjunct to conventional treatments. Overall, the integration of VR into patient care not only enriches the therapeutic experience but also opens new avenues for innovative treatment strategies in the healthcare industry.
As the healthcare industry increasingly integrates Virtual Reality (VR) technology, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize its potential. One of the primary hurdles is the high cost associated with VR hardware and software. Advanced VR systems require significant financial investment, which can be a barrier for many healthcare facilities, especially those with limited budgets. Furthermore, the rapid pace of technological advancement means that these systems can quickly become outdated, necessitating continuous investment.
Technical limitations also pose significant challenges. VR technology demands high computational power and robust internet connectivity to deliver seamless and immersive experiences. Any lag or interruption can detract from the effectiveness of VR-based training or therapy. Additionally, the development of VR content that is both medically accurate and engaging is a complex and resource-intensive process.
Specialized training is essential for healthcare providers to effectively utilize VR technology. This need for training extends beyond simple operational knowledge to include an understanding of how to integrate VR into clinical practice effectively. Without adequate training, the potential benefits of VR may not be fully realized, and there could be an increased risk of improper use.
Regulatory and ethical considerations also play a crucial role in the adoption of VR in healthcare. Regulatory bodies must ensure that VR applications meet stringent safety and efficacy standards. Ethical concerns, such as patient privacy and the potential for over-reliance on technology, need to be addressed to maintain trust and integrity in healthcare practices.
Looking forward, advancements in VR technology could significantly enhance its applications in healthcare. Improvements in hardware affordability and accessibility, coupled with advancements in software development, could mitigate some of the current cost and technical barriers. Future trends may include more sophisticated and realistic simulations, enhanced haptic feedback, and the integration of artificial intelligence to personalize VR experiences.
Continued research and development are vital to overcoming existing obstacles and maximizing the benefits of VR in healthcare. By addressing these challenges head-on, the healthcare industry can harness the full potential of VR technology, leading to improved training outcomes and more effective therapeutic interventions.