Introduction to Autonomous Delivery Vehicles
Autonomous delivery vehicles represent a significant evolution in the logistics and transportation industry, demonstrating the remarkable progress achieved through technological advancements. The concept of self-driving trucks and vans, while once a vision of futuristic science fiction, is now rapidly transitioning into a commercial reality. The history of autonomous vehicles can be traced back to early experiments with automated systems in the 1980s, but it is the recent strides in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sensor technologies that have truly propelled their development.
At the heart of autonomous delivery vehicles lies an intricate network of AI and machine learning algorithms. These systems enable vehicles to interpret vast amounts of data from their surroundings, make real-time decisions, and navigate complex environments with minimal human intervention. The integration of sophisticated sensors, including LiDAR, radar, and camera systems, ensures that these vehicles can detect obstacles, recognize traffic signals, and adapt to varying road conditions.
The motivations behind the adoption of autonomous delivery solutions are multi-faceted. One of the primary drivers is the potential to significantly improve operational efficiency. Autonomous vehicles are capable of operating around the clock without the need for rest breaks, thereby maximizing delivery speeds and reducing transit times. Additionally, the reduction in human error can enhance safety and reliability in logistics operations.
Another compelling reason for the shift towards autonomous delivery vehicles is the reduction in operational costs. Companies can potentially save on labor expenses by minimizing the need for human drivers. Furthermore, the optimized driving patterns of autonomous vehicles contribute to fuel efficiency, reducing overall fuel consumption and associated costs.
Addressing the growing driver shortage in the logistics industry is also a critical factor. As the demand for delivery services continues to rise, the availability of qualified drivers has not kept pace, leading to significant staffing challenges. Autonomous delivery vehicles offer a viable solution to bridge this gap, ensuring that supply chains remain robust and responsive.
In summary, the advent of autonomous delivery vehicles is poised to revolutionize the logistics landscape, driven by advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensor technologies. The pursuit of enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and solutions to driver shortages underscores the growing interest and investment in these innovative systems.
Current State of Autonomous Delivery
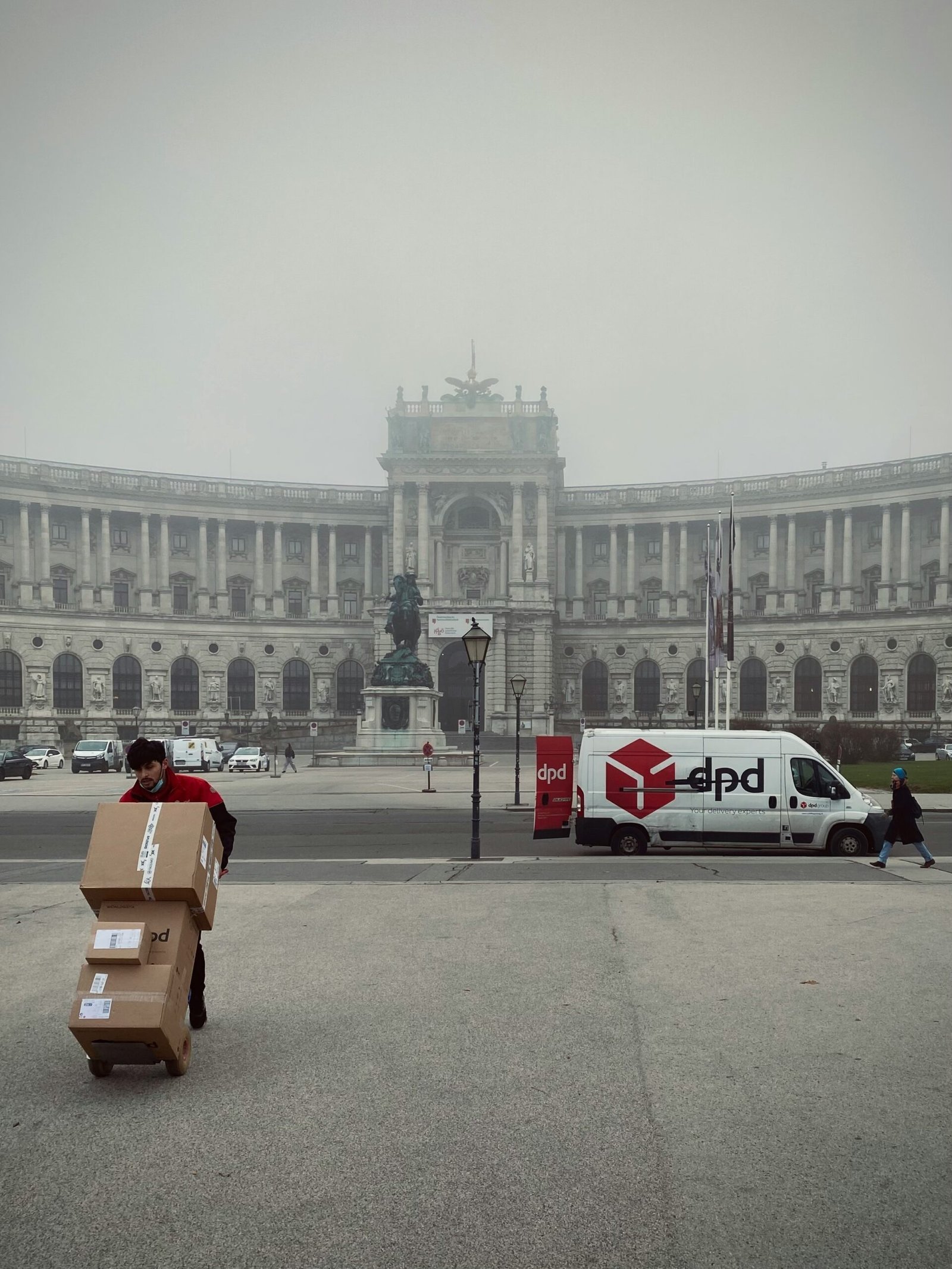
The landscape of autonomous delivery vehicles is rapidly evolving, with several major players leading the charge in developing and deploying these advanced systems. Companies such as Amazon, UPS, and Tesla are at the forefront, conducting pilot programs and investing heavily in autonomous technologies to streamline their logistics operations.
Diverse types of autonomous delivery vehicles are currently being tested and deployed, ranging from small delivery bots designed for last-mile delivery to full-sized autonomous trucks for long-haul routes. For instance, Amazon has been experimenting with its Scout robot, a compact, six-wheeled device capable of navigating sidewalks to deliver packages directly to customers’ doors. In contrast, Tesla’s Semi truck aims to revolutionize long-distance freight transport with its advanced autopilot features and electric propulsion.
UPS has also made significant strides in this arena, partnering with autonomous driving technology companies like TuSimple for the trial of self-driving trucks. These trials have demonstrated the potential for autonomous trucks to improve efficiency and safety in freight logistics, highlighting the practical applications and benefits of these technologies.
Despite these advancements, the deployment of autonomous delivery vehicles faces several regulatory hurdles. Governments and regulatory bodies are still developing frameworks and guidelines to ensure the safe and effective integration of these vehicles into existing transportation systems. Public perception and safety concerns are also critical factors influencing the adoption of autonomous delivery technologies. Incidents involving autonomous vehicles have raised questions about their reliability and the robustness of their safety features.
In addressing these challenges, companies are focusing on rigorous testing and validation of their autonomous systems to build public trust and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. By navigating these hurdles, the industry aims to pave the way for a future where autonomous delivery vehicles become a common sight on our roads, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of delivery services.
Technological Challenges and Innovations
The development of autonomous delivery vehicles, including trucks and vans, is a sophisticated endeavor that encounters numerous technological challenges. One of the primary complexities lies in vehicle navigation. Engineers must develop systems capable of precise and safe navigation through diverse and often unpredictable environments. This involves integrating advanced sensor systems like LiDAR, radar, and cameras, which collectively enable the autonomous vehicle to detect and interpret its surroundings with high accuracy.
LiDAR, for instance, plays a vital role by providing 3D mapping of the environment, allowing the vehicle to identify obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles. The integration of high-resolution cameras further enhances the vehicle’s ability to perceive visual cues such as traffic lights and road signs. However, these sensors alone are not sufficient. The fusion of data from multiple sensors is necessary to create a coherent and reliable representation of the environment, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
A significant technological hurdle is the development of robust software for decision-making processes. Autonomous delivery vehicles must be capable of real-time processing and analysis of vast amounts of data. This software must make complex decisions, such as route planning, obstacle avoidance, and adapting to sudden changes in traffic conditions. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are essential in enabling the vehicle to learn from its experiences and improve its performance over time.
Innovations in battery technology are also crucial, particularly for electric autonomous vehicles. Improved battery life and efficiency are essential to extend the operational range and ensure the reliability of delivery services. Advances in solid-state batteries and fast-charging capabilities are pushing the boundaries, making electric autonomous vehicles more practical and commercially viable.
Another groundbreaking innovation is the development of V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communication. This technology allows autonomous vehicles to communicate with each other, as well as with traffic infrastructure and other road users. V2X enhances situational awareness and cooperative driving, contributing significantly to the safety and efficiency of autonomous delivery systems.
Addressing these technological challenges and leveraging these innovations is vital for the widespread adoption of autonomous delivery vehicles. By overcoming these hurdles, the industry can achieve a new era of efficient, reliable, and safe delivery services.
The advent of autonomous delivery vehicles is poised to revolutionize the logistics and transportation industry. One significant impact will be economic, particularly concerning job displacement and creation. While traditional delivery roles may diminish, the rise of autonomous trucks and vans will generate new opportunities in technology and maintenance sectors. Highly skilled workers will be in demand to design, maintain, and manage these sophisticated systems, thus reshaping the job landscape.
Environmental benefits are another crucial aspect. Autonomous delivery vehicles are often electric or hybrid, leading to reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency. This shift is expected to contribute significantly to environmental conservation efforts, aligning with global initiatives to combat climate change. Furthermore, the precision of autonomous systems ensures optimized delivery routes, which minimizes unnecessary mileage and energy consumption.
As technology advances, consumer expectations will also evolve. The promise of faster and more reliable deliveries will likely become a standard, driven by the efficiency of autonomous vehicles. This shift could lead to a significant transformation in consumer behavior, with an increased preference for online shopping due to the convenience of near-instantaneous delivery. Businesses will need to adapt to these heightened expectations, potentially reshaping the retail landscape.
The integration of autonomous delivery vehicles will also have ripple effects on urban planning and infrastructure. Cities might need to redesign their road networks and delivery hubs to accommodate these vehicles, ensuring they can operate smoothly and efficiently. This could lead to more streamlined traffic flow and reduced congestion, as autonomous vehicles can communicate and coordinate with each other more effectively than human drivers.
Predicting when autonomous delivery services will become mainstream involves considering various factors, including technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and public acceptance. While it is challenging to pinpoint an exact timeline, it is plausible that within the next decade, we will see a significant increase in the deployment of autonomous delivery vehicles. The pace of this transition will largely depend on continued innovation, legislative support, and the ability of society to adapt to these transformative changes.