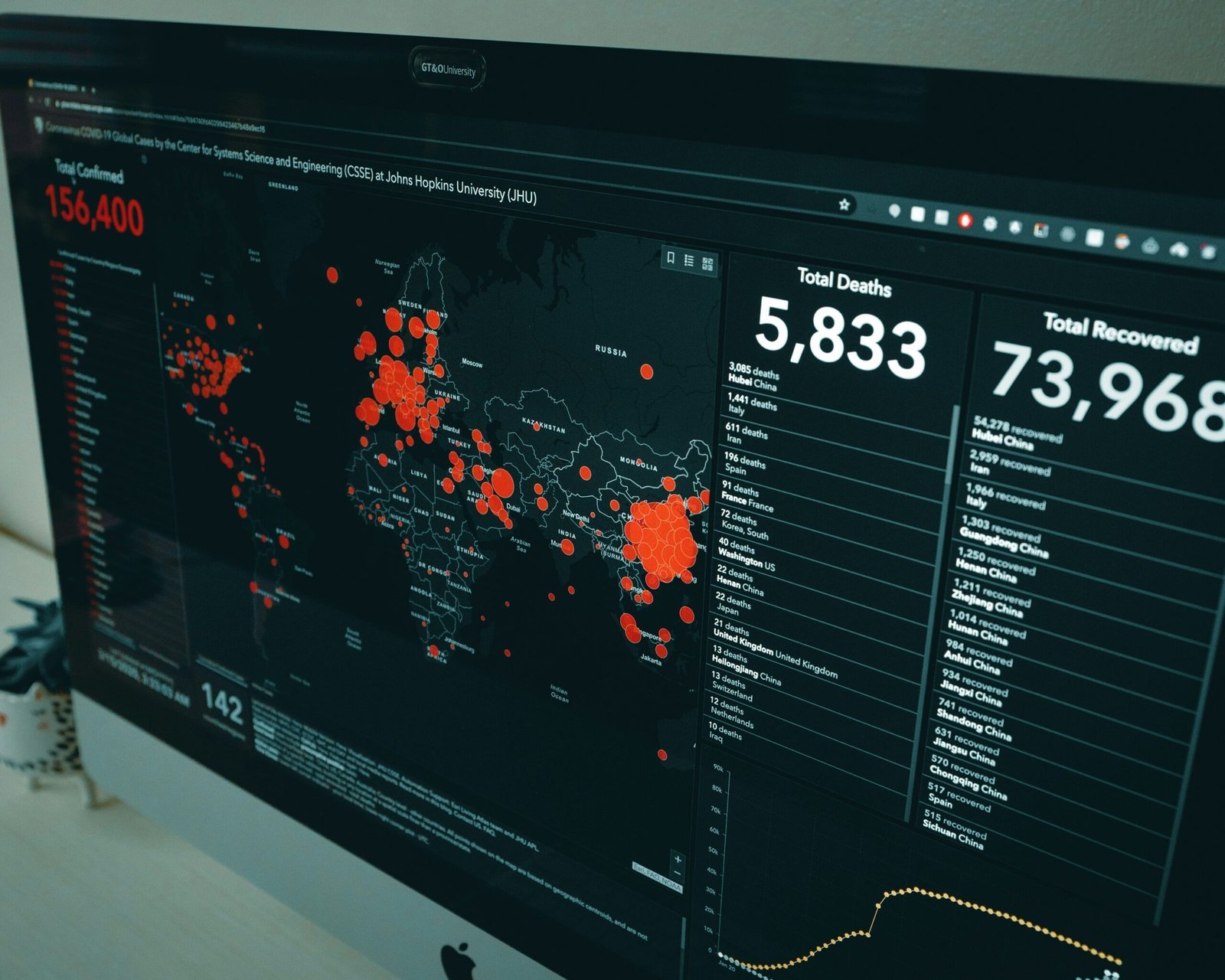
Introduction to Big Data in Healthcare
Big data refers to the vast volumes of structured and unstructured data generated across various sectors, including healthcare. In the healthcare domain, big data encompasses a multitude of sources such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, genomic data, and information from wearable devices. These diverse data sets offer immense potential to transform traditional healthcare practices, making them more efficient and effective.
Electronic health records are a cornerstone of big data in healthcare, providing comprehensive patient information that includes medical histories, treatment plans, and clinical outcomes. Medical imaging, on the other hand, generates extensive data via technologies like MRI, CT scans, and X-rays, adding another layer of valuable insights. Genomic data, derived from DNA sequencing, offers personalized healthcare solutions by identifying genetic predispositions to various conditions. Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, continuously collect real-time health metrics, giving a dynamic and ongoing view of an individual’s health.
The importance of big data in healthcare cannot be overstated. By harnessing these combined data sources, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes through better diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care. Big data analytics involves examining large data sets to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and insights. Through machine learning, healthcare professionals can leverage algorithms to predict patient outcomes and potential risks, enabling proactive healthcare interventions. Predictive modeling, another key concept, uses historical data to forecast future health events, thus aiding in early diagnosis and timely treatment.
Ultimately, the integration of big data in healthcare means more informed decision-making, improved efficiency, and enhanced patient care. As healthcare systems continue to generate vast quantities of data, the importance of developing robust data analytics capabilities becomes increasingly crucial. By capitalizing on these technological advancements, the healthcare sector stands to make significant strides in improving patient outcomes and overall public health.
Applications of Big Data in Healthcare
The utilization of big data in healthcare has revolutionized the industry’s approach to patient care and operational efficiency. One of the most significant applications is predictive analytics, which plays a crucial role in the early diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Through the analysis of vast datasets, healthcare providers can identify patterns and trends that flag potential health issues before they become critical. For instance, algorithms can analyze patient records to predict the likelihood of conditions such as diabetes or heart disease, allowing for early intervention and personalized treatment plans.
Personalized medicine, another major application, leverages genetic information to tailor treatments to individual patients. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can determine the most effective medications and dosages, minimizing adverse reactions and improving outcomes. This approach has shown remarkable success in areas such as oncology, where treatments can be customized based on the genetic profile of a patient’s tumor.
Beyond individual patient care, big data is instrumental in optimizing hospital operations and workflows. Real-time data analysis enables hospitals to manage resources more effectively, from staffing and scheduling to inventory management. For example, predictive models can forecast patient admission rates, allowing hospitals to allocate staff and resources efficiently, reducing wait times, and improving patient satisfaction.
Several real-world examples demonstrate the transformative impact of big data in healthcare. The Cleveland Clinic, for instance, uses predictive analytics to reduce patient readmissions by identifying at-risk patients and providing targeted interventions. Similarly, Mount Sinai Hospital employs big data to predict and prevent hospital-acquired infections, significantly enhancing patient safety.
Key technologies and tools driving these applications include machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and advanced data analytics platforms. Companies like IBM Watson Health and Google Health are at the forefront, offering solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing healthcare systems, enabling providers to harness the full potential of big data.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The integration of big data into healthcare presents several significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure that patient outcomes are genuinely improved. One major concern is data privacy and security. As healthcare data becomes increasingly digitized, the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access escalates. Safeguarding sensitive patient information requires robust cybersecurity measures and stringent compliance with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Ensuring that patient data remains confidential and secure is paramount in cultivating trust and fostering the responsible use of big data in healthcare.
Another challenge lies in the integration of disparate data sources. Healthcare data is often fragmented across various platforms, including electronic health records (EHRs), wearable devices, and genomic databases. Merging these diverse data streams into a cohesive and comprehensive dataset necessitates standardized data formats and interoperability. Lack of standardization can result in data silos, impeding the potential to derive actionable insights from the aggregated data. Establishing uniform data standards and promoting interoperability are crucial steps toward harnessing the full potential of big data.
Ethical considerations also play a pivotal role in the utilization of big data in healthcare. Informed consent is a fundamental ethical principle that must be upheld when collecting and using patient data. Patients should be fully aware of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and the potential implications. Data ownership is another ethical issue, necessitating clear guidelines on who owns the data and how it can be used. Moreover, the potential for bias in predictive models is a critical concern. If the data used to train these models is biased, the predictions and recommendations generated could perpetuate existing disparities in healthcare. Ensuring equitable and unbiased data collection and analysis is essential to mitigate this risk.
Addressing these challenges and ethical considerations is imperative for the responsible and effective use of big data in healthcare. By prioritizing data privacy and security, promoting standardization and interoperability, and upholding ethical standards, the healthcare industry can leverage big data to improve patient outcomes significantly.
Future Trends and the Path Forward
The landscape of healthcare is rapidly evolving, driven by continuous advancements in big data technologies. As we look to the future, several trends stand out that promise to transform patient outcomes significantly. One of the most promising developments is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into healthcare practices. AI and ML can analyze vast datasets, uncover patterns, and make predictive analytics more precise, leading to earlier diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. These technologies are expected to enhance clinical decision-making, reduce errors, and improve patient care efficiency.
Another key trend is the rise of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of these technologies, demonstrating their potential to provide continuous and accessible healthcare. By leveraging big data, telemedicine platforms can offer more comprehensive insights into patient health patterns over time, enabling proactive care management. Remote monitoring devices, which track vital signs and other health metrics, can feed real-time data into healthcare systems, allowing for timely interventions and a reduction in hospital readmissions.
Interoperability between different healthcare systems is also becoming increasingly important. Seamless data exchange across various platforms ensures that healthcare providers have complete and accurate information, which is crucial for making informed decisions. The push for interoperability is supported by emerging standards and protocols that facilitate the secure sharing of health data while maintaining patient privacy. This trend is likely to continue, making coordinated care more effective and efficient.
Policy and regulatory changes will play a pivotal role in the widespread adoption of big data technologies in healthcare. Governments and regulatory bodies need to establish frameworks that promote innovation while safeguarding patient data. Policies that incentivize the use of big data and support the development of interoperable systems will be critical in this regard.
In conclusion, the future of healthcare is poised for a profound transformation driven by big data. To fully realize its potential, ongoing innovation and collaboration among healthcare providers, technologists, and policymakers are essential. By embracing these trends and overcoming associated challenges, the healthcare industry can make significant strides in improving patient outcomes and overall public health.